TL;DR:
- Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease, prevalent in children but affecting adults too, marked by recurrent flares and remissions.
- Symptoms: Persistent itching, erythema, dryness, skin discoloration, cracks, papular lesions, eruptions. Common on elbow/knee folds in children/adults, and scalp/face in infants.
- Causes: Genetic, environmental (pollution, allergens), immunological (IgE overproduction), excessive hygiene, stress, infections, food allergens.
- Treatment: Long-term, includes emollients, glucocorticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors (for sensitive areas), phototherapy, dietary management, and avoidance of irritants. Severe cases may need antibiotics or psychotherapy.
- Complications: Often associated with asthma, allergic rhinitis, and skin superinfections.
Atopic dermatitis is a condition that is quite bothersome and difficult to treat. The symptoms that occur during atopic dermatitis can make daily life difficult, and genes are thought to be the main cause. Nevertheless, it is worth knowing how to recognize the first symptoms so that timely treatment can be undertaken to bring relief by minimizing bothersome symptoms.
What is atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is also known as AZS. It is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. It occurs in both children and adults, but in children it occurs much more frequently. Moreover, in its course it is fraught with recurrent periods with exacerbated symptoms. The hallmark of Disease AZS is persistent itching, all because there is a loss of the protective function of the epidermis. This, in turn, leads to faster evaporation of water, resulting in dry skin. In addition, the skin, not fulfilling its protective function, allows microorganisms and foreign substances to enter the body from the outside. Therefore, the skin is very sensitive to all factors, resulting in the itching characteristic of atopic dermatitis.
Causes of AD
Atopic dermatitis and its causes have not been clearly defined. It is a very complex disease, the causes of which are believed to be genetic as well as environmental and immunological factors. The patient's immune system reacts negatively to small doses of antigens. This leads to excessive production of IgE antibodies, which cause allergic reactions. In turn, environmental causes of AD include allergens and hypersensitivity of the body to pollen or animal dander. In addition, causes of AD can include environmental pollution, infections and food allergens. Another theory attempting to determine the causes of atopic dermatitis speaks of excessive hygiene, that is, raising children in sterile conditions. This, in turn, prevents the proper development of the immune system, which later results in the child's hypersensitivity to various factors. Moreover, the appearance of atopic dermatitis can also be caused by excessive stress and an emotionally hard time in life.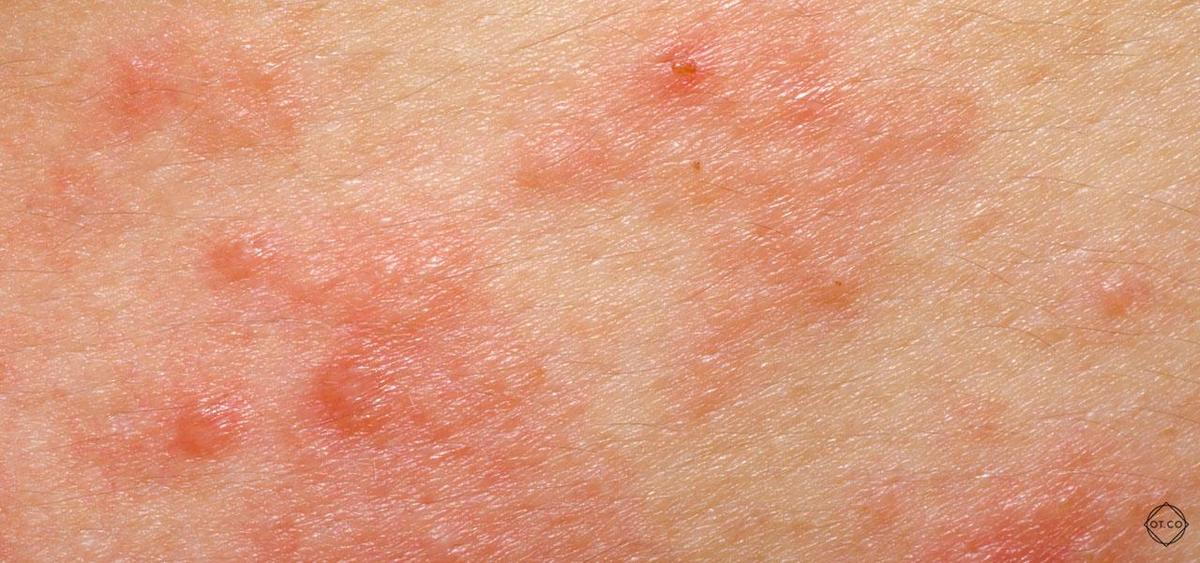
What are the symptoms of atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis gives the first symptoms very early. Therefore, atopic dermatitis in infants is a common case. The typical symptoms of atopic dermatitis are mainly visible skin changes such as erythema, redness and excessive dryness of the skin. In addition, discoloration of the skin and cracks caused by excessive dryness of the skin are very common. The most bothersome of the AD symptoms is itching, which causes constant scratching of the skin. Unfortunately, scratching usually aggravates the irritation. Some patients also develop papular and exudative lesions and may develop skin eruptions. atopic dermatitis Most often, AD manifests itself in the volar surfaces of the extremities, namely the popliteal and elbow pits. These are the sites of appearance of AZS in children and adults. On the other hand, atopic dermatitis most often appears in infants. Characteristic lesions appear on the face and the skin of the entire scalp. It is worth bearing in mind that atopic dermatitis occurs in two periods – extinction and exacerbation, which alternate. In addition, patients suffering from atopic dermatitis often also have other conditions that are caused by AD. These include bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis or superinfection of skin lesions.
What is the course of treatment?
Atopic dermatitis and its treatment is a long-term process that requires cooperation between the patient and the doctor. Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment is used, which aims to repair the damaged epidermis. For this purpose, atopic dermatitis ointment and lubricating creams are used. Such medications are called emollients, and have the additional task of retaining water in the deeper layers of the skin preventing it from drying out.
The treatment of AD also includes phototherapy, which uses ultraviolet radiation to relieve annoying itching. Phototherapy involves irradiating the patient's skin with a specially selected beam of light, which provides relief from the discomfort. In addition, in the case of atopic dermatitis, the use of cosmetics containing irritants, fragrances and preservatives is not recommended. On the other hand, if food allergens are the cause of the ailment, one should pay attention to the meals one eats. During atopic dermatitis, diet is key, as it will help alleviate persistent symptoms. Treatment of atopic dermatitis is also based on steroids or, if necessary, antibiotic therapy. In addition, the most common topical treatment is glucocorticosteroids, which also take the form of ointments. Combined with emollients, they produce extremely effective and quick results. In delicate skin areas like the face, calcineurin inhibitors are also used.
Wet moisturizing compresses and oral antihistamines are also sometimes helpful in relieving symptoms. For patients who, due to the nature of the disease, do not feel mentally well and cannot cope with the constant feeling of itching, psychotherapy is also recommended.
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis is a challenging yet manageable condition with the right care. Recognizing symptoms early allows for effective treatment, easing discomfort and improving daily life. Though its causes remain complex, combining targeted therapies like moisturizers, phototherapy, and personalized diets can make a real difference. Collaboration with specialists ensures better outcomes and relief. While AD can't be cured, understanding its triggers and focusing on long-term management provides control and comfort. Take proactive steps to navigate this condition confidently and improve your quality of life.