TL;DR:
- Syphilis is a bacterial infection (caused by pale spirochete) spread through sexual contact, oral/anal contact, childbirth, and less commonly, blood.
- Symptoms start as genital sores, later progressing to fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, hair loss, and systemic issues if untreated.
- Types:
- Primary: Ulcers on genitals, mouth, or throat (3–4 weeks post-infection).
- Secondary: Rash, sore throat, joint pain, flat warts.
- Latent: Dormant after secondary symptoms subside.
- Congenital: Infection passed from mother to fetus.
- Late: Organ damage after 2 years untreated.
- Diagnosis: Blood/serological tests; home self-tests available.
- Treatment: Penicillin injections (single dose for early stages; prolonged or alternate treatment for late/allergic cases).
- Complications if untreated: Stroke, vision loss, dementia, cardiovascular issues, sexual dysfunction.
An active sex life without protection can lead to contracting syphilis, commonly known as syphilis. Lack of treatment can lead to very serious health consequences, as the disease affects key organs and the functioning of the entire body. What are its symptoms and effects?
Syphilis – basic definition
Syphilis otherwise known as syphilis is a disease caused by the spiral bacteria of the pale spirochete. Infection most often occurs during intimate contact. Although diseases of intimate places are embarrassing, syphilis is not that rare at all. It usually affects young people up to the age of 30, who remain very sexually active. Of course, syphilis can occur in both men and women.
How can you get infected with syphilis?
In the vast majority of cases, syphilis infection occurs during sexual intercourse. However, it is worth bearing in mind that this applies not only to full intercourse, but infection can occur during oral and anal fondling. Moreover, syphilis in pregnant women is also dangerous, as the baby can be infected through the lymphatic and blood vessels, as well as during childbirth. In addition, medical personnel and laboratory workers can also become infected through the blood-borne route. The high infectivity of syphilis occurs in the early stages of the disease. This is also when it is easiest to infect another person. Later, the probability decreases.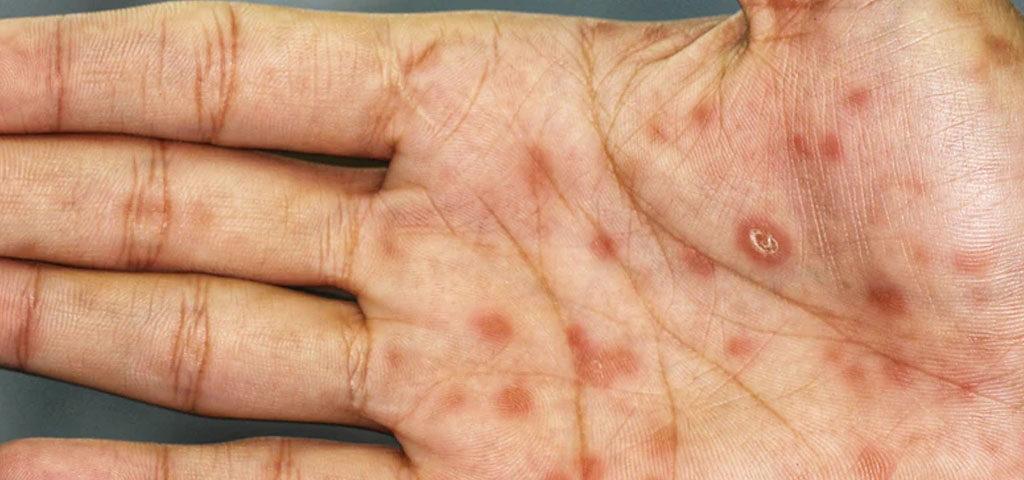
The first symptoms of syphilis
Syphilis gives characteristic symptoms that should not be ignored. These primarily include skin lesions on and around the intimate organs. Thus, syphilis on the penis, labia, or nearby areas has most likely been sexually transmitted. The skin lesions resemble sores with smooth and even edges with oozing serum. It is this that contains a lot of bacteria, which are responsible for the transmission of the disease. It is worth being aware that initially syphilis and symptoms in men or women are the same and, apart from skin lesions, do not give any additional symptoms. Because of this, the moment of infection is often overlooked, and the disease goes dormant after 9 weeks. In addition, other symptoms of syphilis at a later stage include the possibility of appearance:
- larger lymph nodes,
- fever,
- malaise,
- excessive hair loss – syphilitic alopecia,
- brittleness of nails,
- discoloration on the skin – syphilitic vitiligo.
Syphilis can also develop on the arms and legs and can appear on the face and other parts of the body.
Types of syphilis
There are several forms of the disease syphilis syphilis. These are congenital syphilis, primary syphilis, secondary syphilis, latent syphilis and late syphilis. Each of these runs slightly differently, and the symptoms of syphilis in men and women for each type can look different.
Primary syphilis – what is it?
Primary syphilis, or initial syphilis, occurs 3 to 4 weeks after infection. It manifests itself as small skin lesions of an ulcerative nature. Such sores can appear not only on the genitals. Syphilis occurs on the tongue, face, or throat. Most often, syphilis and its symptoms in women appear on the clitoris, labia, and on the cervix. In men, on the other hand, syphilis appears on the penis, testicles and scrotum.
Secondary syphilis – symptoms
Symptoms of secondary syphilis include a rash and sore throat. The rash does not itch, but appears on the hands, feet and all over the body. It is pink and takes the form of red papules and pink spots. In addition, flat condylomas appear around intimate areas. Syphilis can also give symptoms such as headaches, sore throat, enlarged lymph nodes, or bone and joint pain.
Congenital and latent syphilis.
Congenital syphilis is said to occur when a child is infected in fetal life or during birth. On the other hand, latent syphilis on the face or genitals is the third stage of the disease, when the primary and secondary symptoms subside. However, the bacteria still remain in the body.
Late syphilis – how does it manifest itself?
Late syphilis is referred to when two years have passed since infection. If proper treatment has not been carried out during this time, further health problems may develop. Late syphilis and its symptoms include myocarditis problems, ulcerative skin lesions, joint inflammation and more.
Diagnosis and treatment of syphilis
Syphilis is a disease that requires appropriate treatment to be able to prevent serious health consequences. Of course, the treatment depends primarily on the type of syphilis.
Diagnosis of syphilis
Syphilis on the genitals is quite characteristic, but due to the location of the skin lesions, it can be difficult to spot. If the disease is suspected, a syphilis test can be performed. These are serological tests from the blood. Often a test for HIV, HCV and syphilis is performed together. You can also buy ready-made tests from pharmacies to diagnose yourself at home.
Syphilis – treatment of early and advanced stages of the disease.
For primary, secondary and latent early stage disease, syphilis in men and women is treated by administering penicillin. Usually a single injection of this antibiotic is sufficient. Therefore, if syphilis gives the first symptoms, do not delay a visit to the doctor. Quick response and administration of an antibiotic makes the treatment of syphilis effective.
On the other hand, if syphilis lasts for more than a year, treatment may be slightly different. Additional doses of penicillin are administered, or another syphilis drug is also implemented if there is an allergy to the popular antibiotic. It is important to keep in mind that syphilis and its treatment at home without consulting a doctor will not be possible, making you vulnerable to health consequences. In the case of sexually active people, it is likely that the ill person has infected his partner. Even if the characteristic symptoms of syphilis in men and women have not appeared, preventive treatment is recommended.
Consequences of untreated syphilis.
If you already know what syphilis looks like, consult a doctor about any skin lesions of an ulcerative nature. Syphilis in the throat or on the genitals, as well as syphilis on the nose, are just as dangerous. Complications they can cause include stroke, headaches, partial hearing loss and even vision problems. In addition, the consequences of not treating the disease include dementia, incontinence problems, myocarditis and sexual dysfunction in men. It is for these reasons that it is advisable to use prophylaxis and avoid situations in which one can become infected with syphilis, and take treatment as soon as one notices skin lesions.
Conclusion
Syphilis is a serious disease that spreads easily without proper awareness or precautions. From its early symptoms, like sores and rashes, to its various stages, syphilis can deeply harm your health if left untreated. Prompt testing and treatment, often as simple as a penicillin injection, are key to preventing severe complications. Take care of your body, recognize the risks, and seek medical support at the first sign. Your health depends on it.