TL;DR:
- Eczema Overview: Eczema is a non-contagious inflammatory skin condition affecting the epidermis and dermis, often with an allergic or genetic basis.
- Causes: Eczema can be endogenous (genetic) or exogenous (triggered by allergens in food, cosmetics, or materials).
- Symptoms: Redness, itching, swelling, dry skin, small sores, scaling, and blistering. It progresses in acute, subacute, or chronic phases.
- Affected Areas: Commonly occurs on hands, face, feet, legs, and abdomen.
- Diagnosis: Visual skin inspection, patient interviews, allergen-specific IgE blood tests, and contact skin tests.
- Treatment: Avoid allergens, use prescribed creams, moisturize regularly, consider desensitization, or immune-modulating treatments for severe cases.
- Care: Use hypoallergenic dermocosmetics for moisturizing and rebuilding the skin’s barrier. Regular care helps prevent recurrences.
Any changes in the appearance of the skin can indicate eczema. This is a disease that can be very diverse in nature and severity. It is worth knowing what its symptoms are, when to see a doctor and how to treat and reduce unpleasant and annoying skin changes.
What is eczema?
Under the term eczema there are a number of dermatological skin diseases. They are characterized by inflammation of the skin and in most cases have an allergic basis. The inflammation develops in the superficial layers of the skin, that is, within the epidermis and the papillary layer of the dermis. Often eczema on the hands or other parts of the body is called eczema. [read url="https://otcoclinic.com/offer/" text="Atopic dermatitis – causes, symptoms, treatment"]. Superficial inflammation of the skin can occur almost all over the body. Eczema of the hands, face, or feet is common. The course of the disease depends on its location, as well as its severity. Eczema on the face can run a very mild course and be initially trivialized, or its course can be acute and cause great discomfort. What is important about this condition is that eczema cannot be contracted from another person.
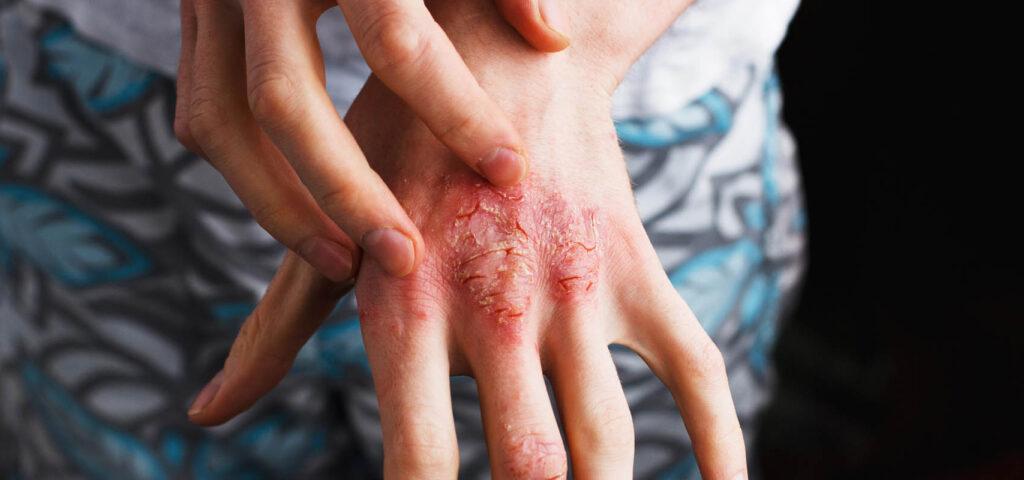
What causes the appearance of eczema?
The causes of eczema on the legs, hands, face and other areas of the skin are varied and sometimes difficult to clearly identify. It is believed that the genetic basis determining the condition of the skin is of great importance here. Moreover, allergies and environmental factors are also considered the main cause of eczema. For this reason, two basic types of eczema are distinguished. These are endogenous eczema caused by genetic factors and exogenous eczema caused by contact with an allergen. Sensitizing substances can be both the foods eaten, as well as materials or substances contained in cosmetics.
Main symptoms of eczema
Eczema and its symptoms can take on a different character. It all depends on the type and severity of the disease. However, among the first symptoms that may indicate that the skin lesions are eczema on the hands or any other part of the body are local redness of the skin, a feeling of itching and a noticeable local swelling on the skin. In addition, it is common for eczema to have very dry skin, small sores on the surface of the skin, and in some cases a pathological exudate in the form of mostly pus. Eczema of the hands and feet can also manifest itself in the appearance of small papules on the skin surface, peeling and great discomfort. Depending on the severity of the characteristic symptoms there are three phases of eczema. These are acute, subacute and chronic. In the case of a severe allergic reaction, erythema and small and suppurating blisters appear on the skin just a few hours after contact with the allergen. On the other hand, in the case of the subacute phase, there is a slight peeling of the skin, and scabs become visible at the site of the erythema. The chronic phase, on the other hand, is said to occur when inflammation persists for a long time, leading to epidermal hyperplasia and quite severe scaling. In addition, itching of the skin is very strong and contributes to frequent scratching and skin eruptions.
Occurrence of eczema
The inflammatory skin condition can affect both children and adults of different ages. Eczema in children is as frequently diagnosed as it is in adults. Its course can take on different stages of severity and cause considerable discomfort in daily life. Eczema appears on the eyelids, feet, hands, back, legs, as well as the abdomen. However, it is worth knowing that eczema in a baby mostly resolves with age.
Eczema vs. psoriasis
Flaky skin can give symptoms similar to psoriasis. For this reason, it is important to visit a doctor to distinguish between these two completely different skin conditions. Psoriasis is caused by an overactive immune system that causes the epidermis to mature, die and flake off at an accelerated rate. The implication is that dead epidermal cells do not have enough time to exfoliate and detach on their own, as new epidermal growth is constantly being stimulated. [read url="https://otcoclinic.com/offer/" text="Psoriasis – causes, course of psoriasis, treatment"]. As a result, there is an overlap of skin layers, which causes the appearance of papular skin lesions. So, as you can see, eczema and psoriasis are separate diseases caused by different factors. The way they are treated is also different, so these diseases should not be considered identical due to similar symptoms.
Diagnosis of eczema
To be able to start effective treatment and alleviate the symptoms of eczema, it is crucial to diagnose it accurately. Eczema on the feet, hands, or face is diagnosed on the basis of a visual inspection of the skin condition, as well as an extensive interview with the patient. Information about the frequency of lesions, comorbidities and genetic conditions is crucial. In order to know exactly what factors cause an allergic reaction on the surface of the skin, the doctor may order allergologic tests, such as contact skin tests. However, this method is not used every time, because here the patient is exposed directly to the allergen, which can expose him to a severe allergic reaction. An alternative in diagnosis is the currently used measurement of allergen-specific IgE antibody concentrations in the blood. Their detection allows to determine precisely which agent triggers an allergic reaction in a person. Measurements are made from blood drawn in the traditional way. They are therefore completely safe and non-invasive.
Treatment of eczema
The treatment of eczema should be individually tailored to the patient. It is important to determine the type of eczema, as well as to conduct diagnostic tests. Eczema and its treatment when an allergenic factor is identified is primarily based on avoiding the allergen. Therefore, the measurement of allergen-specific IgE antibody concentrations in the blood plays such an important role. In order not to expose yourself to an allergic reaction, it is necessary to carefully check the composition of cosmetics, washing products or consumed articles and avoid those in which the allergen is found. It is also possible to carry out desensitization treatment. It is usually offered to patients who are allergic to a specific element. In addition, in severe cases, treatment affecting the immune system is included. However, this is a procedure that strongly interferes with the entire organism and its functioning. For years, many scientists have been searching for answers to the question of how to effectively treat eczema. Currently, the most popular method of treatment is limiting contact with the allergenic agent and alleviating skin symptoms.
Skin care with eczema
Eczema on the legs, hands, face, or any other part of the body requires proper care. This is because it helps relieve persistent symptoms and soothe inflamed skin. Well-chosen cosmetics allow to support the process of rebuilding the protective barrier of the epidermis, as well as to protect the skin from external factors, including allergens. Eczema in infants and adults should be alleviated using dermocosmetics. These are products that do not contain allergens in their composition and are carefully tested. They must meet very strict standards and undergo numerous tests to assess their safety. What's more, they are hypoallergenic, and there are no chemicals, perfumes or dyes in their composition. Eczema skin care cosmetics have strong moisturizing, regenerating, restorative and protective properties. They can be purchased in good online and stationary drugstores, as well as in pharmacies. However, it is not worth experimenting, but ask your doctor about the cosmetic that will work best in your case. Some creams or gels can only be purchased by prescription, and those generally available may not be sufficient for acute and severe eczema. Of course, in alleviating the symptoms of eczema that have already appeared on the skin, regularity plays an important role. Care with appropriate cosmetics should be carried out in accordance with the doctor's recommendations and until the skin lesions have fully subsided. You should also be aware that eczema, despite the complete elimination of symptoms, can recur after some time. It is then said and its remission. Eczema is a dermatological skin infection that should not be underestimated. Quickly undertaken diagnosis will allow to know the allergenic factor and exclude it from daily life. Thus, annoying symptoms can be resolved, and unsightly and embarrassing skin lesions disappear.
Conclusion
Eczema is more than just skin irritation; it’s a complex condition with diverse causes. Recognizing its symptoms, understanding triggers, and seeking proper medical care are vital for managing flare-ups. From diagnosis to personalized treatments and diligent skin care, every step matters. While eczema may recur, proactive management and avoiding allergens can greatly reduce discomfort. Don’t settle for temporary relief—focus on long-term strategies to protect your skin and improve your quality of life.