TL;DR:
- Melanoma: A malignant skin cancer caused by pigment cells, often mistaken for moles, with high metastasis potential. Early detection offers a 97% cure rate.
- Causes: UV/UVB radiation (sunlight, tanning beds), genetic predisposition, fair skin, frequent sunburns (esp. in youth). Increasingly affects young people.
- Prevention: Avoid sun exposure (11 AM–4 PM); use sunscreen, sunglasses, and hats; avoid tanning beds (≥50% risk increase with 1+ visit/month); protect children's skin.
- Symptoms: Changes in mole color, size, shape; itching; bleeding; black/red lesions. Regular self-exams and dermatologist checkups are key.
- Diagnosis: Dermatoscopy and biopsy confirm malignancy. Watch for new or worrisome skin changes.
- Treatment: Surgery removes lesions, possibly lymph nodes. Advanced stages may require immunotherapy or chemotherapy.
- Facts: Melanoma can occur on skin, mucous membranes, eyes, or nails; early detection yields 90% cure rate. Risk is higher for fair-skinned individuals.
Melanoma is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers. It is a lesion that appears on the skin, which is often overlooked, all because it resembles a mole, of which everyone has many. Therefore, it is worth knowing what characterizes melanoma, so that if you suspect its appearance, you can make an appointment with a specialist as soon as possible and start treatment.
What is melanoma?
Melanoma is a malignant tumor that mostly affects the skin. However, it also happens to affect the mucous membranes of the nose and mouth. In addition, there is also black nail cancer and vascular membranes of the eye. Its origin is the pigment cells, or melanocytes, found throughout the body. Melanocytes are primarily responsible for skin pigmentation, or skin color, which especially changes when exposed to UV radiation. melanoma However, pigment cells also affect the color of the iris and hair. Melanoma of the skin is a highly malignant neoplasm, giving metastasis both to nearby lymph nodes and distant ones. That's why prevention and early diagnosis are so important, with a very good chance of a complete cure.
Causes of melanoma
Melanoma and its causes of its origin by doctors are mainly defined as UV and UVB radiation. This is sunlight and artificial radiation such as in tanning beds. A great influence on the formation of melanoma is short and intense exposure to the sun and burns, especially at the age of 15. In addition, there are also certain genetic conditions that favor the development of skin cancer. These are primarily a fair complexion with numerous nevi, as well as blond hair and blue eyes. Also, the appearance of melanoma in the family can increase the chance of getting the disease. Typically, skin cancer affects the elderly, but there are cases at a young age. In addition, there is an increasing rate of growth of the disease precisely among young people.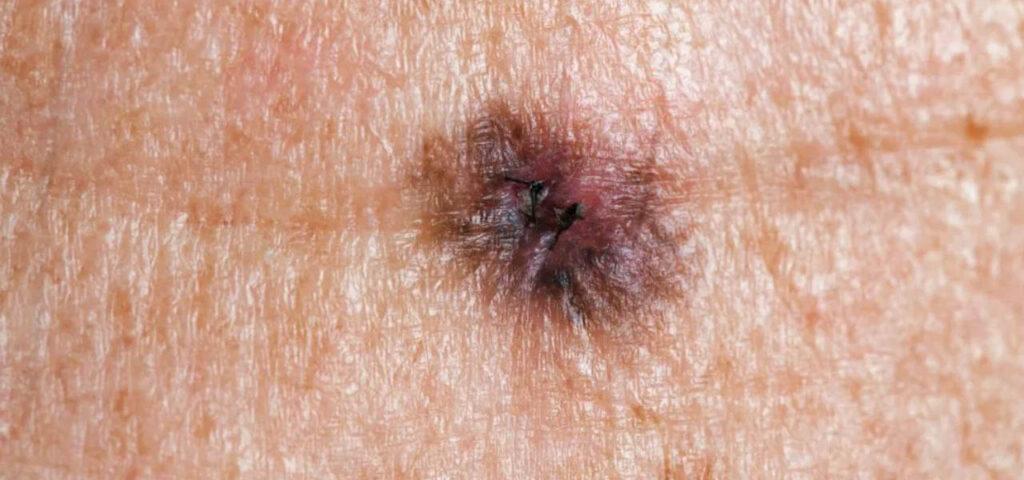
Prevention
People in the high-risk group in a special way should follow several rules to reduce the risk of the disease. First of all, intense exposure of the body to the sun should be avoided, especially between 11 am and 4 pm, when it is particularly strong. It is also important to use a high-protection sunscreen and wear sunglasses and head coverings. Special attention should be paid to protecting the skin of children and adolescents, as prolonged exposure to the sun at such a young age increases the risk of skin cancer. Of course, the use of tanning beds is not recommended, as more than one visit per month increases the risk of melanoma by up to 50%.
How to recognize melanoma?
Many people, especially those with multiple moles, ask doctors the question – how diagnose melanoma. Although it is a malignant skin cancer, its diagnosis is very simple. All because it appears on the surface of the skin in a visible place. For this reason, the best way to quickly diagnose melanoma is to look at your skin regularly. Each newly formed nevus, such as a mole and a growth, should be observed. If it changes color, shape and size, an appointment should be made with a doctor for a thorough examination.
melanoma diagnosis Melanoma vs. a mole is a difficult lesion for many to distinguish. That's why it's a good idea to pay attention to the color when observing the body. In melanoma, the color of the lesion is black or red, and its size and shape increase with time. In contrast, moles are brown and are unlikely to enlarge. In addition, melanoma and its symptoms are itching and bleeding, which should not be underestimated under any circumstances. If the lesion is questionable, an appointment should be made with a dermatologist. Using a dermatoscope, he will be able to quickly and painlessly identify the type of lesion. Further diagnosis, in case of suspicion of melanoma – skin lesion biopsy. Based on it, it is determined whether the lesion is malignant melanoma, and if so, at what stage of development.
How does the treatment of melanoma proceed?
The treatment of melanoma does not look the same in every case. First of all, it depends on the stage of the tumor and the location of the tumor, whether it is subungual melanoma or on the skin or mucous membranes. If the melanoma is detected relatively quickly, then treatment is simple, and most importantly offers a 97% cure rate. Treatment is primarily surgery, performed after a biopsy that confirmed the presence of cancer.
During the procedure, the entire lesion and biopsy scar are removed, as well as a two-centimeter reserve of healthy skin. If the melanoma is at a more advanced stage and has penetrated more than 1mm into the skin, a biopsy of nearby lymph nodes is also performed. If cancer cells are detected in them, then a lymphadenectomy is performed, which involves the complete removal of the lymph nodes. melanoma removal In addition, in some cases, immune therapy is also used, which affects the patient's immunity, thereby helping the body fight the cancer. If the melanoma has metastasized to other parts of the body, chemotherapy is also used.
Facts and myths about melanoma
It is worth bearing in mind that melanoma can appear on skin with an unchanged surface or on an existing nevus. In Poland, melanoma accounts for 5% to 7% of the percentage of all skin cancers and 1% of overall cancers. Due to the increasing number of cases, there has been some misinformation about melanoma. Here are the facts and myths that play a big role in diagnosis and treatment. Melanoma appears only in the skin – fact Melanoma is a skin cancer that mostly appears on the skin. However, it is worth bearing in mind that it can appear anywhere melanocytes are present, i.e. on mucous membranes, intimate areas and on the eyeball and nails. Therefore, one of the most effective methods of detecting melanoma is regular observation of the body and emerging lesions. Melanoma is an incurable cancer – a myth In most cases, especially detected early, up to 90% of patients are cured. Treatment of melanoma in the first stage is limited to surgery, which removes the lesion along with a safe margin of healthy tissue. Melanoma appears only on existing nevi – myth Melanoma can appear both on moles and other nevi that have been on the patient's skin for years, but also on healthy skin without any lesions. Therefore, any new and worrisome lesion should be examined to rule out cancer. All moles must be removed quickly – myth The appearance of a new mole on the skin does not mean that it must be removed for prevention. Only lesions that show worrisome features when examined with a dermatoscope or with the confirmed presence of cancer cells should be removed. Melanoma is one of the most aggressive cancers – fact Skin cancer such as melanoma is among the most malignant. Unfortunately, it shows a high capacity to metastasize, even distantly. All due to the fact that it is transmitted via lymph nodes and blood vessels. People with fair skin are at higher risk of developing melanoma – fact People with fair skin, blond or red hair and blue eyes are at increased risk of melanoma. All because light complexion is much more sensitive to sunlight and UV radiation. It is much more easily subject to sunburn, which at a young age increases the risk of later developing melanoma. Only large moles are dangerous – myth Often patients pay most attention to large and visible lesions. However, it is not only dark and protruding moles that should cause concern. It turns out that flat and small lesions are much more likely to be dangerous. In addition, if a mole is new or has also been on the skin for several years and begins to itch, grow or bleed, you should immediately visit a dermatologist for diagnosis. Avoidance of the sun is a method of melanoma prevention – fact People, especially those at risk, should pay attention to skin protection during sun exposure. Use high sunscreens, head coverings and avoid prolonged exposure to the sun directly. Also, giving up tanning beds will help reduce the risk of melanoma. People who use tanning beds more than twice a month increase their risk of melanoma by up to 50%.
Conclusion
Melanoma is a serious yet preventable cancer if caught early. This article covered its causes, symptoms, prevention methods, and treatment options. Regular skin checks and limiting UV exposure can save lives. Don't ignore changes in moles or new lesions—early action leads to a high cure rate. Protecting your skin and staying vigilant are your best defenses against melanoma.






