TL;DR:
- Seborrheic warts are benign skin lesions that commonly appear on the face, neck, torso, and scalp, especially in adults over 30. They are painless, usually harmless, and do not increase cancer risk.
- Causes: Unknown, but associated with genetic predispositions, sebum overproduction, poor hygiene, age, sun exposure, and hormonal changes.
- Appearance: Raised, smooth, or rough nodules varying in size (millimeters to centimeters) and color (white, yellowish-brown, beige). Often found singly or in groups.
- Treatment Options:
- Cryotherapy: Freezes warts with liquid nitrogen.
- Electrocoagulation: Uses electric current to destroy cells.
- Laser removal: Destroys wart pigment with precise radiation.
- Home Remedies: Include apple cider vinegar, tea tree oil, aloe vera, vitamin A, and salicylic acid but require caution and dermatologist consultation for safety and effectiveness.
A seborrheic wart is a benign skin lesion that often appears on the face, neck, torso and other areas of the body. It usually takes the form of a raised, smooth or uneven spot or nodule, ranging from a few millimeters to a few centimeters in diameter. Seborrheic wart does not have a specific, unambiguous cause, while some factors contributing to its formation can be distinguished. Although seborrheic warts are usually benign and unrelated to the risk of tumorigenesis, they can be an aesthetic problem or cause some discomfort, especially when they appear in areas exposed to constant irritation.
Seborrheic wart – causes of formation.
**The causes of seborrheic warts are mainly related to processes in the sebaceous glands and in the structure of the skin.However, the unequivocal cause of this ailment is unknown. Increasing attention is being paid to a genetic basis, as a familial occurrence of warts has been noted. Other factors that contribute to their formation include:
- sebum overproduction – seborrheic warts are caused by excessive production of a fatty substance, by the sebaceous glands of the skin. This can lead to clogging of the glands' mouths and the formation of skin lesions,
- improper hygiene – the accumulation of dead skin cells can contribute to the clogging of the sebaceous gland mouths, creating conditions conducive to the formation of seborrheic warts,
- genetic factors – if someone in the family has had these types of skin lesions, it is more likely that others in the family will also develop them,
- age – they often appear in elderly people. Skin aging processes, such as loss of elasticity, can promote their formation,
- sun exposure – prolonged exposure of the skin to sunlight can affect the development of a variety of skin changes,
- hormonal changes – including those occurring during puberty, pregnancy or menopause, can affect the activity of the sebaceous glands.
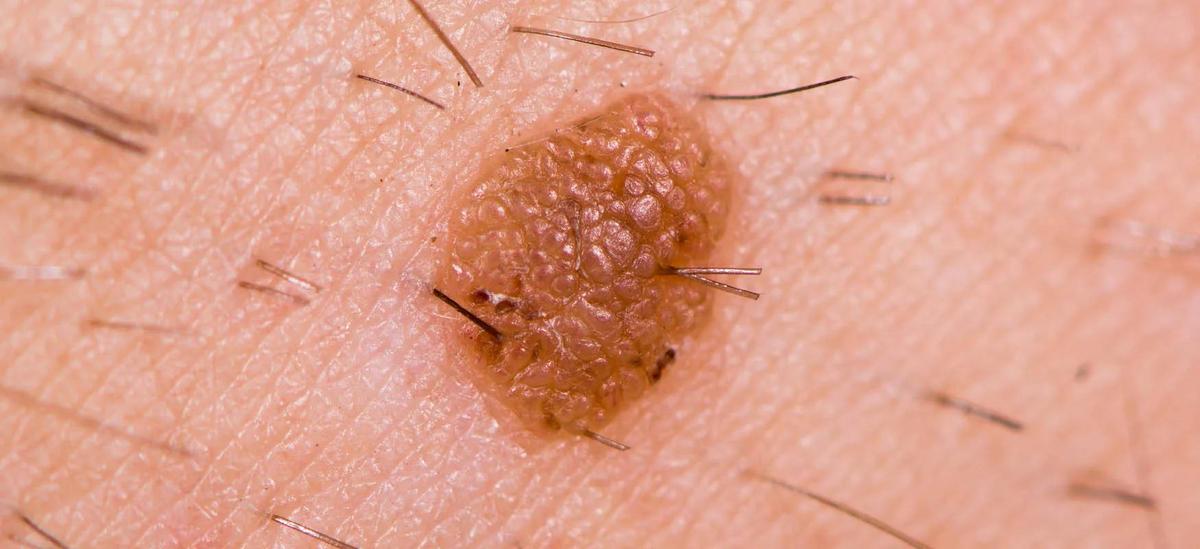
What does a seborrheic wart look like?
Seborrheic warts have a distinctive appearance that makes them easy to identify. They can take the form of raised, rounded nodules or flat spots of various shapes and sizes, usually ranging from a few millimeters to centimeters. Their color can vary, but usually takes on shades of pearly-white, yellowish-brown or beige. The surface of seborrheic warts can be smooth, slightly uneven or rough. Some lesions may have structures in the form of scales, which gives them a distinctive appearance. In terms of location, they can occur on various areas of the body, including warts on the neck, wart on the face, the trunk, and the scalp are often present. They can appear singly or in groups. They are usually painless and do not cause any discomfort. They also do not tend to itch or bleed. The described skin lesions are most common in adults over the age of 30. No relationship was observed between gender and the frequency of appearance of seborrheic growths on the scalp and body. It is worth noting, however, that although seborrheic warts are usually benign, it is always important to consult a dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis and assess whether the lesions found on the body are safe and not cancerous in origin. The doctor may recommend appropriate treatment or decide whether to remove the wart, especially if the patient is uncomfortable with its presence or is concerned about aesthetic goals.
Seborrheic wart on the head
Seborrheic warts can also occur on the scalp. They usually do not pose a serious health risk, while they often give patients a feeling of discomfort, so they are removed for aesthetic reasons. Moreover, removal should be considered when the wart is exposed to mechanical factors such as rubbing or irritation.
Seborrheic wart treatment and removal.
Although a lesion such as a seborrheic wart does not require specialized treatment because it is benign in nature, patients often choose to have them removed. This is especially true when the lesions occur in the head area or other visible areas. They are often a source of complexes or discomfort. Seborrheic wart removal should be carried out by a professional dermatologist or a doctor specializing in dermatology. There are several methods of removing the lesion. Among the most popular treatments are laser removal and cryotherapy.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is a procedure that freezes seborrheic warts, which involves freezing them using liquid nitrogen. The first step is a consultation with a doctor, who will evaluate the wart and decide whether cryotherapy is an appropriate method of removal. Before the procedure, the area around the wart must be cleaned. Using a special cryotherapy device, a stream of liquid nitrogen is precisely directed at the wart. The substance is at a very low temperature, which freezes and damages the affected cells. Usually, after a few days to a week, the frozen wart falls off the surface of the skin. In some cases it may be necessary to repeat the procedure, especially if the wart was not fully removed with the first treatment. After cryotherapy, local redness, swelling and a burning sensation may occur, but these symptoms usually subside within a few days. It is important to avoid scratching or irritating the treated area.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is one method of removing seborrheic warts, using an electric current to destroy the wart cells. Consultation with the doctor is followed by preparation of the skin area for the procedure. In some cases, local anesthesia may be used to minimize discomfort.
The doctor uses an electrocoagulator, a device that generates an electric current, to safely destroy wart cells. The current causes coagulation, a process of truncating the proteins in the cells, leading to their destruction. Special skin care may be recommended after the procedure. Local pain, redness or mild swelling may be felt, but these symptoms usually subside within a few days. It is important to follow the doctor's instructions for caring for the treated skin area and monitor any changes.
Laser removal of seborrheic warts.
Another effective method of removing seborrheic warts is laser therapy. The procedure uses laser radiation to intentionally remove the wart cells. At the outset, the doctor performs a thorough evaluation of the skin, rules out any contraindications and confirms whether laser wart removal is appropriate for the case. The skin around the wart is properly prepared, and then, using a special laser device that emits light at a specific wavelength, the light is absorbed by the pigment in the wart cells, leading to its destruction.
The laser procedure allows precise control of the destruction of wart cells, minimizing the risk of damage to adjacent tissues. After the procedure, redness, slight swelling or a burning sensation may occur, disappearing within a few days. Your doctor may recommend special skin care after the procedure, including the use of soothing creams or avoiding exposure to the sun.
Seborrheic wart home remedies.
Although home remedies can help alleviate the symptoms of seborrheic wart, it is important to remember that professional evaluation and dermatological treatment are usually the most effective. If you decide to use home remedies, apply them carefully and monitor your skin's reaction. Here are some home remedies:
- apple cider vinegar – can help relieve the symptoms of warts. Apply a small amount of vinegar to the wart with a cotton ball. You can do this several times a day,
- tea tree oil – has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Dilute a few drops of tea tree oil in a carrier oil (for example, coconut oil) and apply to the skin lesion,
- aloe vera – has soothing and moisturizing properties. You can apply aloe vera gel to the wart several times a day,
- vitamin A – vitamin A for seborrheic warts can help exfoliate them. This substance is an ingredient in many anti-aging creams. Before using such preparations, especially prescription ones, consult a dermatologist,
- Salicylic acid – salicylic acid for seborrheic warts also has exfoliating properties. You can use preparations containing this ingredient, such as creams or liquids. However, remember to follow the instructions and not to use it excessively.
Remember that consulting a dermatologist before starting any home therapy is always recommended, especially if you have doubts about the nature of the wart or if you do not observe improvement after using home remedies.
Conclusion
Seborrheic warts are common, harmless, and often linked to genetics, aging, or skin changes. While they don't pose health risks, they can cause discomfort or aesthetic concerns. Options like cryotherapy, laser removal, and electrocoagulation offer effective solutions, while home remedies may provide some relief. Always consult a dermatologist to ensure proper diagnosis and guidance. Taking care of your skin and addressing changes can improve comfort and confidence.