TL;DR:
- Drooping eyelid (ptosis) has congenital and acquired causes.
- Congenital: abnormal development of the upper eyelid elevator muscle.
- Acquired: aging, trauma, neurological diseases, chronic inflammation.
- Surgery for ptosis (blepharoptosis) takes 1-2 hours, is under local anesthesia or short-term sedation.
- Surgical techniques: resection/replacement of the tendon or suspension of the eyelid on the frontalis muscle.
- Before surgery, required tests (morphology, coagulation, sugar) and consultation with the surgeon.
- Contraindications: clotting disorders, uncontrolled hypertension, active infections, advanced diabetes, tumors.
Did you know that a drooping eyelid can affect your confidence and eye health? If you’re considering drooping eyelid surgery, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, I’ll describe exactly how such a procedure works, its benefits, and what to look out for before and after surgery. Learn the details and gain confidence in your quest for the perfect look!
What are the causes of drooping eyelid (ptosis)?
A drooping eyelid, also known as ptosis (Latin: ptosis), can have various causes. Understanding the source of the problem is key to choosing the right treatment.
Congenital causes of drooping eyelid
The first group of causes are congenital anomalies. Congenital ptosis often results from abnormal development of the upper eyelid elevator muscle. In such cases, the problem occurs from birth. Children with congenital ptosis may have difficulty seeing, which can affect their visual development. Therefore, proper diagnosis and prompt medical intervention are important to avoid future vision problems.
Acquired causes of drooping eyelid
The second group of causes includes acquired ptosis. The most common form is senile ptosis, which occurs with age. It is the result of weakness or damage to the upper eyelid elevator muscle and stretching of its tendon. Other acquired causes include trauma, neurological diseases and changes associated with chronic inflammatory conditions of the eye.
Recognizing the cause of a drooping eyelid is of great importance, as it affects the choice of the appropriate treatment. In any case, whether congenital or acquired ptosis, consultation with a specialist is crucial. Detailed examinations help determine whether the problem can be solved by surgery, or whether it requires a different therapeutic approach.
How does surgery for a drooping eyelid proceed?
Drooping eyelid surgery, also known as blepharoptosis surgery, is a complex process that can significantly improve the appearance and functionality of the eye. To understand how this procedure is performed, it is useful to focus on two main aspects: the description of the surgical procedure and the surgical techniques used during the procedure.
Description of the surgical procedure
The procedure for drooping eyelid surgery usually takes one to two hours and is performed under local anesthesia or brief intravenous sedation. Before the operation, the surgeon carefully examines the function of the eyelid lift muscle, the effectiveness of which determines the choice of surgical technique. If this muscle functions properly (i.e., its function exceeds 4 mm), the operation consists of resection or relocation of the elevator tendon. On the other hand, if the muscle has less function, the preferred method is to suspend the eyelid from the frontalis muscle using autologous fascia or synthetic materials.
Surgical techniques used during the procedure
During the procedure, the surgeon makes an incision parallel to the eyelid margin to minimize visible scarring. Subsequently, resection of excess fatty tissue and displacement and reattachment of the levator muscle are the key steps of the operation. The entire process is controlled by assessing the position of the eyelid margin during surgery. In complicated cases where there are differences in the location of the tendon of the levator muscle, the operation can be combined with blepharoplasty performed under intravenous sedation.
The course of surgery for a drooping eyelid thus depends on a number of factors, including the age of the patient, the cause of the ptosis and any comorbidities. It is also worth remembering that full correction and symmetry are not always possible, and some cases may require reoperation for optimal results.
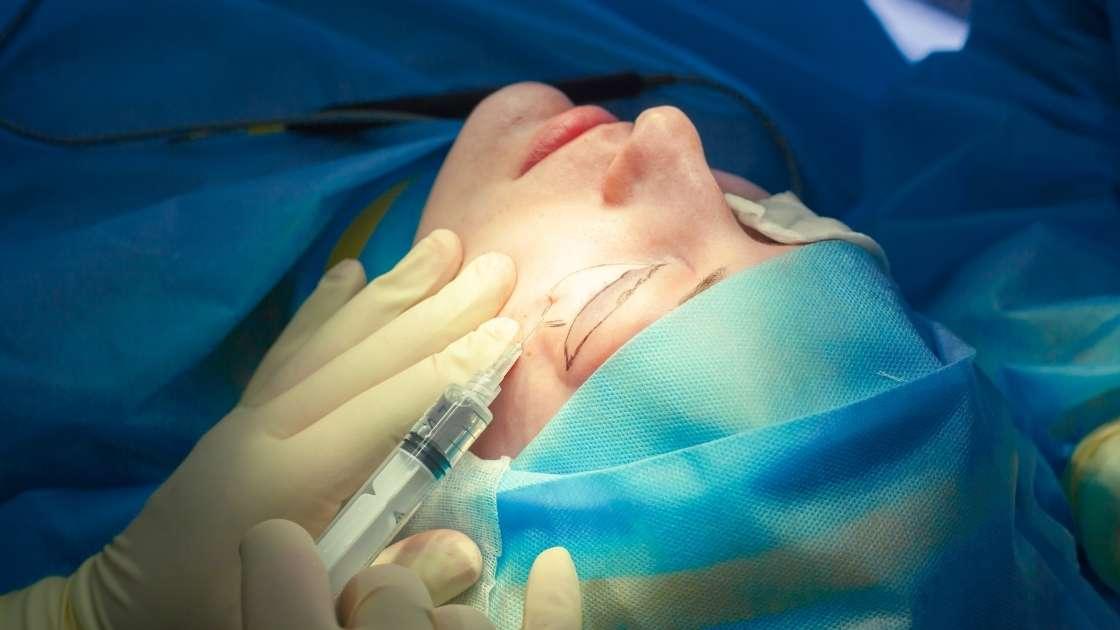
What are the preoperative recommendations?
When you decide to undergo drooping eyelid surgery, preparation for the procedure is key. You need to keep in mind a few important steps so that the surgery goes smoothly and without complications.
Preparing the patient before surgery
Preparation for drooping eyelid surgery begins with a consultation with your surgeon. During this visit, expectations are discussed, and an explanation of the entire process is provided. The surgeon will take a detailed medical history, assess the condition of your eyelids and the function of the eyelid lift muscle. It is important to inform the doctor about all medications and supplements being taken, as some of them can affect blood clotting.
Necessary preoperative examinations
Several tests are necessary before surgery. Most commonly, these include a blood count, a coagulation test and blood sugar levels. The results of these tests will allow the doctor to assess whether you are ready for surgery and whether there are any health contraindications. If there are any medical conditions, such as hypertension or diabetes, they must be well controlled before proceeding with surgery.
Remember that proper preparation before drooping eyelid surgery is key to achieving the best results. Consult your specialist to learn more about preoperative procedures and recommendations.
How does a drooping eyelid surgery proceed?
Surgery for a drooping eyelid, also known as blepharoptosis, is crucial not only from an aesthetic point of view, but also for improving the visual field. The procedure is precise and consists of several steps, which I would like to discuss in detail to dispel any doubts.
Description of the surgical procedure
The operation usually takes one to two hours and is performed under local or brief intravenous anesthesia. The surgeon makes a small incision on the eyelid, parallel to its edge. He then proceeds to resect the excess fat and tissue, which allows for a better elevation of the eyelid. An important step is the disconnection and reattachment of the eyelid elevator muscle, which allows for precise positioning of the eyelid. Once these steps are completed, the wound is carefully sutured, minimizing the risk of scarring.
Surgical techniques used during the procedure
Depending on the function of the eyelid elevator muscle, different surgical techniques are used. When the function of the muscle is more than 4 mm, anterior surgery with muscle resection or tendon repositioning is preferred. On the other hand, when the muscle function is less than 4 mm, an eyelid suspension technique to the frontalis muscle using the patient’s own fascia or synthetic materials is recommended. Each of these methods has its own advantages and is chosen based on the individual needs of the patient and the results of detailed preoperative examinations.
Surgery for a drooping eyelid is a complex process that requires precise evaluation and planning. Surgeons carefully analyze the function of the elevator muscle and other factors to choose the most appropriate method, ensuring the effectiveness of the procedure and patient satisfaction.
How is drooping eyelid surgery performed?
Drooping eyelid surgery, also known as blepharoptosis, is a procedure to improve the aesthetics and function of the eyelids. I will outline how the entire process works, from preparation for surgery to the various surgical techniques used during the procedure.
Description of the surgical procedure
The surgery begins with a thorough evaluation of the function of the eyelid lift muscle. Based on this assessment, a decision is made on the appropriate surgical technique. The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia or brief intravenous anesthesia, which means that the patient is conscious but not in pain.
Initially, the surgeon makes an incision parallel to the edge of the eyelid. He then performs fat resection, separation and displacement of the levator muscle. The key moment is to determine the correct eyelid height, which is done by assessing the position of the eyelid during the procedure. The entire process usually takes 1 to 2 hours.
Surgical techniques used during the procedure
Depending on the function of the eyelid lift muscle, the surgeon may use different techniques. If the function of the muscle is more than 4 mm, surgery on the anterior part of the muscle with resection or displacement of the tendon is preferred. If the function of the muscle is weaker, less than 4 mm, the frontalis muscle suspension method is used, using the patient’s own fascia or synthetic materials.
In some cases, the techniques can be combined with blepharoplasty, or plastic eyelid correction, which further improves the aesthetics of the eyelids. Each of these techniques aims not only to improve the appearance, but also the function of the eyelids, which is crucial for patients with advanced drooping eyelids.
Detailed information on the surgery techniques can be found here.
What are the contraindications to drooping eyelid surgery?
The decision to have drooping eyelid surgery is a major step that requires consideration of various health factors and conditions that may preclude surgery.
Conditions that rule out the possibility of surgery
The first step before surgery is a thorough analysis of the patient’s health. Some conditions absolutely rule out the possibility of surgery. These include blood clotting disorders, which can lead to serious complications during surgery. Uncontrolled hypertension also poses a serious risk to patient safety. In addition, any active skin infections in the eye area preclude the procedure due to the risk of spreading the infection.
Health and age contraindications
In addition to the above conditions, there are other health contraindications to consider. Advanced diabetes, cancer, autoimmune diseases and endocrine disorders can pose serious risks during surgery. People with a tendency to form hypertrophic scars, or keloids, should also avoid this type of surgery.
The age of the patient is another key factor. Although there is no rigid age limit, elderly patients with additional medical conditions may be at higher risk for complications. It is also important for pregnant and breastfeeding patients to postpone surgery.
Before deciding to undergo surgery, it is always recommended to consult with an experienced specialist who will conduct a full health assessment and help decide whether the procedure is safe. For more information on eyelid surgery, you can visit this link.
How does a drooping eyelid surgery work?
Sagging eyelid surgery, also known as blepharoptosis, is a complex procedure that requires precision and expertise. It is often performed to improve the appearance and restore normal eyelid function, which can have a huge impact on the patient’s comfort and quality of life.
Description of the surgical procedure
During surgery, the surgeon makes an incision parallel to the eyelid margin. This incision allows access to the internal structures of the eyelid, including the eyelid elevator muscle. Through this incision, the surgeon can perform fat resection, excision and reattachment of the elevator muscle to improve its function. The entire procedure usually takes 1 to 2 hours and is performed under local or short-term intravenous anesthesia.
Surgical techniques used during the procedure
The choice of surgical technique depends on the function of the levator muscle. If the function of the muscle is more than 4 mm, the surgeon may choose to operate on the anterior portion of the levator muscle by resecting or relocating its tendon. In cases where the muscle function is less than 4 mm, the preferred method is to suspend the eyelid to the frontalis muscle using autologous fascia or synthetic materials.
Each of these techniques is designed not only to improve aesthetics, but also to restore eyelid function. Note that full correction and symmetry are not always possible, and some cases may require reoperation.
More information on the safety of the procedure can be found here.
Conclusion
In summary, we have discussed the causes of drooping eyelid, including congenital and acquired causes. We have listed the stages of surgery and the surgical techniques used in the procedure. We also provided preoperative and postoperative recommendations and discussed the effects and risks of the surgery. Effectively performed surgeries produce lasting and satisfactory results, making life more comfortable. Understanding the surgical process and recommendations helps you make an informed decision.