TL;DR:
- Prenatal tests are conducted during pregnancy to monitor the baby's health, divided into non-invasive (safe, no risk) and invasive (only if genetic issues are suspected).
- Benefits: Early disease detection, potential in-womb treatment, identification of congenital and developmental defects (tests done as early as 10-14 weeks).
- Non-invasive tests: Include genetic ultrasound, blood tests (PAPP-A, SANCO, IONA, PANORAMA) to assess risk of genetic issues; some determine baby’s sex.
- Invasive tests: Include amniocentesis (amniotic fluid), chorionic villi biopsy, and cordocentesis (cord blood), conducted after abnormalities found in non-invasive tests.
- Diseases detected: Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, Edwards syndrome, Turner syndrome, heart defects, and more.
- Recommended for all pregnant women, especially those over 35, with family/genetic risks, or IVF pregnancies.
The period of pregnancy is a special time for a woman and her family. Information about the expected baby often causes euphoria and is an eagerly awaited moment. However, it is worth bearing in mind that this is a very demanding time for a woman. It is essential to change existing habits and to perform regular examinations. Among them are prenatal tests. What do they consist of and is it worth opting for them?
What are prenatal tests?
Prenatal tests, are tests that are performed before the baby is born, that is, during pregnancy. Prenatal tests are divided into non-invasive and invasive. The latter are performed only in cases of reasonable suspicion of a genetic defect in the child. Invasive prenatal tests are carried out in a hospital and under the care of experienced doctors. However, in most cases it is not necessary and non-invasive prenatal tests are performed. They do not require interference with the body of both mother and child. For this reason, their performance does not cause any side effects and is completely safe.
What do we gain from undergoing prenatal testing?
The main reason why prenatal tests are performed is to learn about the health and development of the child already at the fetal stage. ** Early detection of a child's disease even makes it possible to start treatment while the child is still pregnant and reduce the risk of developing the disease.** In addition, in some cases it is possible to completely cure the child while still in the womb. Performing prenatal examinations in a timely manner and by experienced specialists makes it possible to identify fetal birth defects with high probability or to eliminate them completely. In addition to congenital defects, prenatal testing also allows detection of developmental defects. Primenatal tests are performed at a very early stage, as between 10 and 14 weeks of pregnancy. This is the first trimester of pregnancy, so the test is usually performed one month after the first symptoms appear. Subsequent tests are also performed at a later stage of pregnancy.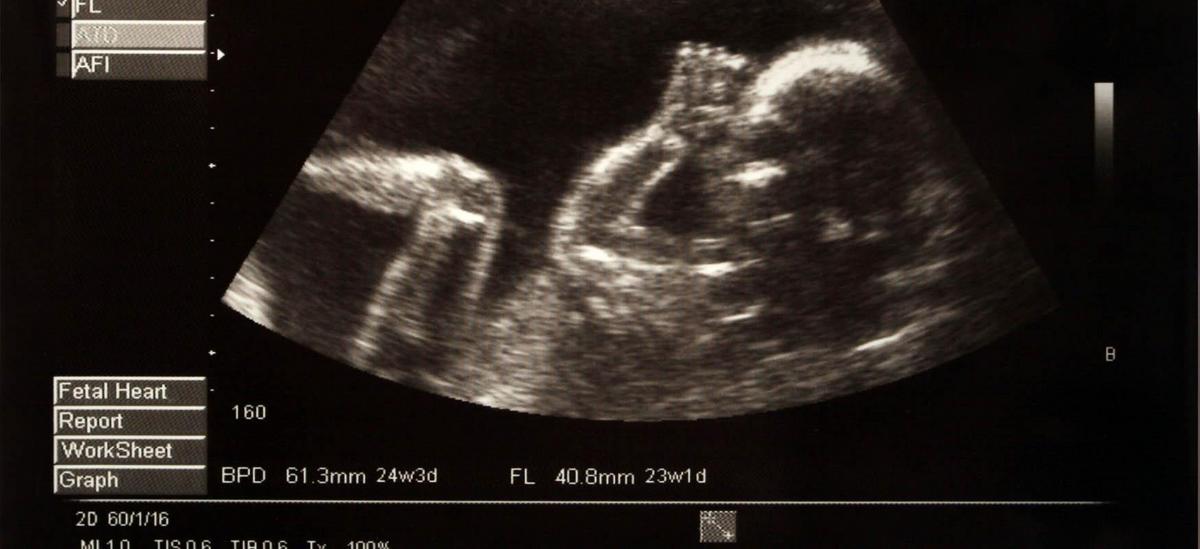
Non-invasive prenatal testing
Non-invasive prenatal tests mainly include genetic ultrasound, double test (PAPP – A), SANCO (NIFTY), triple test and IONA and Panorama. Genetic ultrasound is slightly different from the traditional one. It is performed on a more sensitive machine and by an experienced doctor. Its execution time is longer and can take up to an hour. The test allows you to check the gestational follicle and yolk sac, the dimensions and shape of the fetal organs, heart function, placenta, or the umbilical cord and the length of the femurs and nasal bones. ultrasound in pregnancy The double test, on the other hand, involves drawing the mother's blood and determining the concentration of the pregnancy substances PAPP – A and free beta – hCG. Another SANCO test helps determine the baby's risk of fetal trisomy. The test is also based on blood drawn from the mother. Similar to the trisomy test as well, except that here the concentration of beta – HCG, pregnancy protein AFP and free estriol are analyzed from the blood sample. Another IONA test allows to assess the risk of genetic defects, and the PANORAMA test is a screening test that gives the possibility to obtain important information about the course of pregnancy from the 9th week. The sex of the baby can also be determined with this test.
Invasive prenatal testing
Invasive tests are performed when certain abnormalities in fetal development are detected during non-invasive tests. The first of the invasive tests is amniocentesis, which involves the collection of amniotic fluid. This is done under ultrasound guidance. The material collected allows to determine chromosomal abnormalities. However, this test can be performed at the earliest between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy to reduce the risk of complications and miscarriage. Another ** prenatal test of an invasive nature is a chorionic villi biopsy.** During the procedure, a fragment of the chorionic villi, the membrane that co-forms the placenta, is taken. It is done through the vaginal or transvaginal route. The last of the invasive tests is cordocentesis, which involves the collection of cord blood by puncturing the umbilical cord. This test is performed after the 20th week of pregnancy.
What diseases can be detected through prenatal testing of pregnancy?
Prenatal tests allow for a very broad diagnosis and high accuracy when it comes to detecting diseases at an early stage of pregnancy. They allow to confirm or exclude such diseases as **Down syndrome, hemophilia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis, Edwards syndrome, meningeal and umbilical hernia, Patat syndrome, Huntington's chorea, heart and urinary tract defects, anemia and Turner syndrome.
When should prenatal testing be performed?
Every woman expecting a baby should undergo prenatal testing. However, there are certain cases in which prenatal testing should be mandatory. These include a woman's age above 35, a previous pregnancy that ended in a child with genetic or developmental defects, and in the case of genetic diseases in the family. In addition, if one of the prospective parents has a chromosomal aberration, in vitro fertilization occurred and the results of the necessary tests raise doubts, it is worth opting for prenatal testing. They will allow doctors to react quickly and start treatment as early as possible. In addition, they allow future parents to adequately prepare for the birth of a sick child, in order to provide the best possible conditions for its development and treatment. ** Prenatal examinations should be performed by every mother-to-be, especially in the case of a higher probability of congenital and progressive genetic defects.** However, it is worthwhile, in the case of suspected abnormalities in the development of the fetus, to use the services of doctors with extensive experience, who will support the patient and explain what exactly the various tests consist of and conduct them reliably and accurately.
Conclusion
Prenatal testing is a powerful tool that helps ensure a healthy pregnancy. It can detect potential genetic or developmental issues early, allowing for timely interventions or treatment. Non-invasive tests offer safe, accurate insights, while invasive tests are used only when absolutely necessary. Every expecting mother should consider these tests, especially in high-risk cases. Partnering with experienced doctors ensures reliable results and peace of mind. Taking proactive steps through prenatal testing benefits both the mother and her baby, setting the stage for a healthier future. Don't overlook this essential part of pregnancy care.