TL;DR:
- What are tonsil stones? Hardened growths in tonsil crypts caused by lingering food debris, dead cells, and bacteria; can grow up to 3 cm and weigh 50g, causing discomfort and difficulty swallowing.
- Symptoms: Sore throat, swollen/red tonsils, metallic taste, severe bad breath, foreign body sensation, cough, visible white lumps (if large).
- Causes: Poor oral hygiene, reflux, smoking, diet high in sugar, chronic/untreated tonsillitis.
- Treatment: Mouth rinses (sage, hydrogen peroxide), manual removal, ENT intervention (e.g., cryptolysis with lasers), or tonsil removal.
- Complications: Chronic inflammation, throat abscess, ear infections, swallowing issues, potential blood infections.
- Prevention: Oral hygiene, tonsil rinses, and flossing, though complete prevention is difficult without surgery.
Small-sized, hard, irregular pebble-like lesions are nothing more than tonsil stones. This condition is unpleasant insofar as it can cause bad breath, infections in the mouth, as well as giving the impression of a foreign body in the throat. What are tonsil stones caused by and how can they be cured?
tonsil stones – what are they?
Almond stones are hardened growths that form in the recesses of the palatine tonsils. The tonsils are responsible for protecting against the penetration of dangerous microorganisms and pathogens into the body. They also produce antibodies and cytokines that regulate inflammation. Each tonsil, meanwhile, consists of lymphoid tissue and has about 30 crypts that increase its surface area and protective functions. ** Tonsils are formed due to the occurrence of bacterial infections of the throat and tonsils, including tonsillitis.** Recurrent or untreated inflammation, on the other hand, leads to the formation of adhesions and scars on the tonsils. These, in turn, impede the process of self-cleaning of the crypts when speaking and swallowing saliva. Lingering food debris, exfoliated epithelium and many microorganisms calcify and harden over time, which is the reason for the formation of lumps that are difficult to remove naturally. They usually have a light, yellowish hue with a diameter of up to a few millimeters. In extreme situations, however, almond stones can reach up to 3 centimeters in diameter and weigh 50 grams. Such lesions are already a major impediment to free speech and swallowing. It so happens that the congenital, defective structure of the crypts can promote the formation of tonsil stones. Factors that facilitate the formation of stones also include poor oral hygiene, reflux, as well as smoking and a diet rich in simple sugars.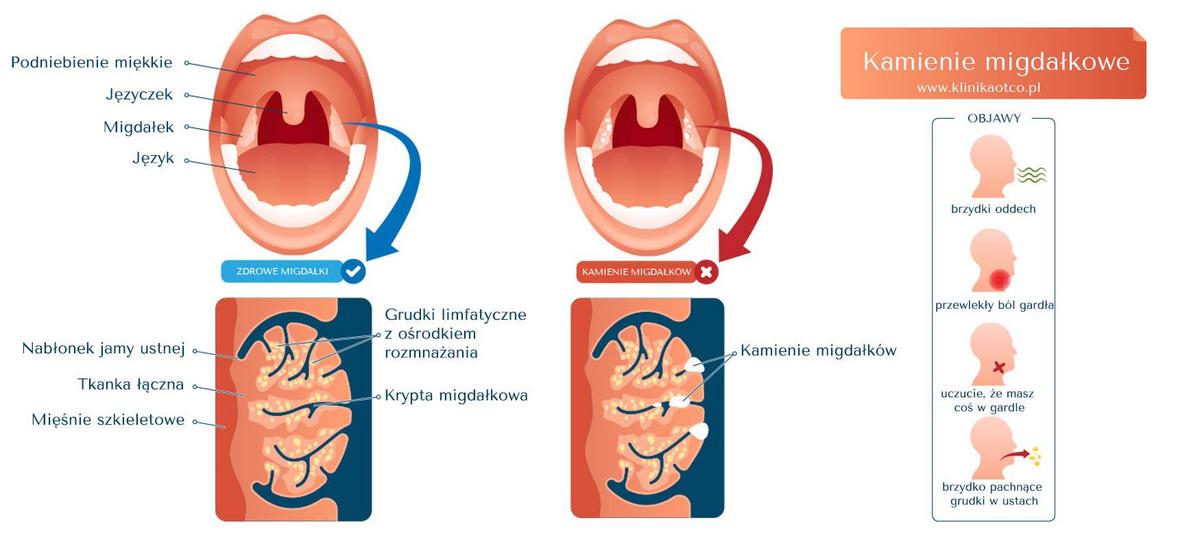
What are the symptoms of tonsil stones?
The presence of tonsil stones can be easily diagnosed by such symptoms as:
- A sore throat that makes it difficult to swallow saliva. Sometimes it can radiate toward one ear.
- Swelling and redness of the tonsils – signs of inflammation.
- Metallic aftertaste in the mouth that interferes with the perception of tastes.
- Unpleasant breath with a typical putrid mouth odor. This is the result of the proliferation of oral bacteria that cause putrefactive processes. As a result, sulfur-containing odorous substances are produced. Unpleasant mouth odor cannot be eliminated by oral hygiene, chewing gum and mouthwash.
- A foreign body sensation in the throat and reflex coughing. Small-sized tonsil stones are very often removed just by coughing or coughing away.
- In the case of large tonsil stones, white lumps are visible.
What are the causes of tonsil stones?
tonsil stones are usually formed due to:
- accumulation of food debris,
- accumulation of dead blood cells,
- the impact of anaerobic oral bacteria.
Tonsil stones are lesions consisting of accumulated food debris, exfoliated epithelial cells, dead white blood cells or bacteria and microorganisms. The tonsils, on the other hand, are distinguished by their flexible structure, which makes the stones difficult to feel in the initial stage. However, if their size exceeds a centimeter, one can feel discomfort and vomiting reflexes. Larger tonsil stones, on the other hand, can cause inflammation, so the problem should not be ignored.
What is the diagnosis of tonsil stones?
Tonsil stones can very easily be mistaken for tonsillitis, however, then antibiotics have no effect on treatment. This is not a bacterial infection, which can be combated just with an antibiotic, and this drug will only worsen the condition of the patient. Treatment of tonsil stones is chronic in nature.
How to treat tonsil stones?
A short-term method of treating tonsil stones is to rinse them by regularly rinsing the mouth with herbal infusions that have anti-inflammatory properties. These include sage, hydrogen peroxide solution and antiseptic fluids. Stones can also be removed mechanically with a stick or spatula. However, this technique is quite tedious, as it requires a skilled hand, and incompetent removal can irritate the mucous membrane, causing pain. In severe cases, tonsil stones require a visit to an ENT specialist and a procedure to remove the calcifications with shallowing or closing of the crypts. This is known as cryptolysis, which is performed using a CO2 ablative laser, cryosurgery or radiosurgery. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The specialist damages the mucous membrane, resulting in remodeling of the tonsil tissue and shallowing of the large crypts. The lingering contents are then removed, and the small crypts are closed.
The results of the procedure can be seen after two weeks – a month. That's how long it takes for the tissue within the tonsils to remodel. Sometimes surgical removal of the tonsils is also necessary.
Are tonsil stones dangerous to health?
The problem of the occurrence of tonsil stones affects up to 10% of the population. Usually, apart from unpleasant breath affecting limited social contacts, stones do not cause dangerous health complications. They are also not dangerous if they spontaneously detach and the patient accidentally swallows them. However, if the calcifications are large and untreated, severe inflammation of the throat, tonsils or blood infection can occur.
What complications do untreated tonsil stones cause?
Constantly lingering stones in the tonsil crypts can cause persistent chronic inflammation, not only in the tonsils, but also in the middle ear. They are also a cause of pharyngitis, throat abscess and severe swallowing disorders. Tonsil stones are also a potential source of inflammation of the blood, which eventually leads to endocarditis.
How are tonsil stones prevented?
It is virtually impossible to effectively prevent the development of tonsil stones. People struggling with chronic inflammation can expect that surgery to remove the tonsils will be one salvation. However, it is worth remembering that proper oral hygiene and frequent brushing and flossing can help. Rinsing the tonsils and mouth along with cleaning them with hydrogen peroxide can remove food debris and bacteria, which in turn reduces the risk of stones. It is also important to remember that a number of other conditions can cause pain in or around the tonsils and may resemble the symptoms seen with tonsil stones. These include tonsillitis, gum disease and tooth decay.
Why should tonsil stones be treated?
Open tonsil crypts are the cause of many problems. It is the tonsil stones that may be present in them, which cause an inflammatory reaction, enlargement, soreness of the tonsils and the sensation of a foreign body in the mouth. These changes are also the cause of an unpleasant, embarrassing odor from the mouth. It is also worth remembering that the first appearance of symptoms that may indicate tonsil stones is usually a harbinger of a constant recurrence of problems. Then, even after eliminating the stones by coughing, squeezing or rinsing, the lesions on the tonsils take from 1 to 20 days to recover. So it's worth consulting a specialist to help deal with the problem effectively.
Conclusion
Tonsil stones are more than just a minor annoyance; they can lead to chronic discomfort and bad breath while signaling deeper oral health issues. Though good hygiene can reduce the risk, persistent cases may require professional removal or cryptolysis to prevent complications like inflammation or infection. Recognizing and treating tonsil stones early is key to avoiding long-term problems. If left unmanaged, they can impact both your health and quality of life. Don’t ignore the signs—addressing the issue promptly is the best way forward.






