TL;DR:
- Urticaria (hives) is a common skin condition causing itching, burning, and red, raised blisters; its symptoms usually resolve quickly but can reappear.
- Types include cold, cholinergic (sweat-induced), contact, pressure, sun, and heat urticaria.
- Causes range from allergens, stress, infections, medications, insect bites, and UV exposure to physical factors like pressure or temperature changes.
- Acute urticaria resolves within days; chronic urticaria lasts over 6 weeks, often requiring a doctor’s care.
- Treatment includes antihistamines, steroids, cyclosporine, and in chronic cases, omalizumab (an anti-IgE antibody).
- Chronic urticaria may be linked to allergens and requires clinical trials for further evaluation.
- Solar urticaria is managed by limiting UV exposure and using sunscreen or covering clothing.
- Consult a doctor for severe or recurring symptoms.
Urticaria is a common skin condition. It is usually associated with food allergies, but this is not the only cause of its occurrence. In its chronic form, urticaria can cause tremendous feelings of embarrassment, sleep disturbances and functioning at work. Fortunately, there are effective ways in medicine to get rid of this problem.
What is urticaria?
Hives is nothing more than one of the most common skin diseases, which poses a huge diagnostic problem for doctors from many specialties. Patients then face sudden skin lesions resembling those after being burned by nettle – hence the name of the disease. The skin lesions that occur with urticaria show great variability and dynamism. They can take the form of a few lesions, or occupy the skin of the entire body. The rash during urticaria looks like tiny blisters with a reddened base. Hives are also distinguished by severe itching. However, the lesions do not persist on the skin for a long time – they appear quickly and disappear just as quickly – giving way to new ones. Acute urticaria lasts a maximum of a few days.
What symptoms indicate the presence of urticaria?
The name of urticaria is not accidental – the typical symptoms are familiar to anyone who has encountered unpleasant nettle leaves or been stung by an insect at least once in his life. Urticaria can be recognized by the fact that there are raised, reddened, pale blisters on the skin, resembling the changes that occur when the skin comes into contact with nettles. urticaria Urticaria is not painful and usually resolves after a few days without leaving scars or skin discoloration. However, this common ailment can effectively make it difficult to function, as the blisters on the body cause itching. Other symptoms may include a burning or stinging sensation, and when pressed against the center of a reddened blister, the lesions turn white. Urticaria can also move across the skin.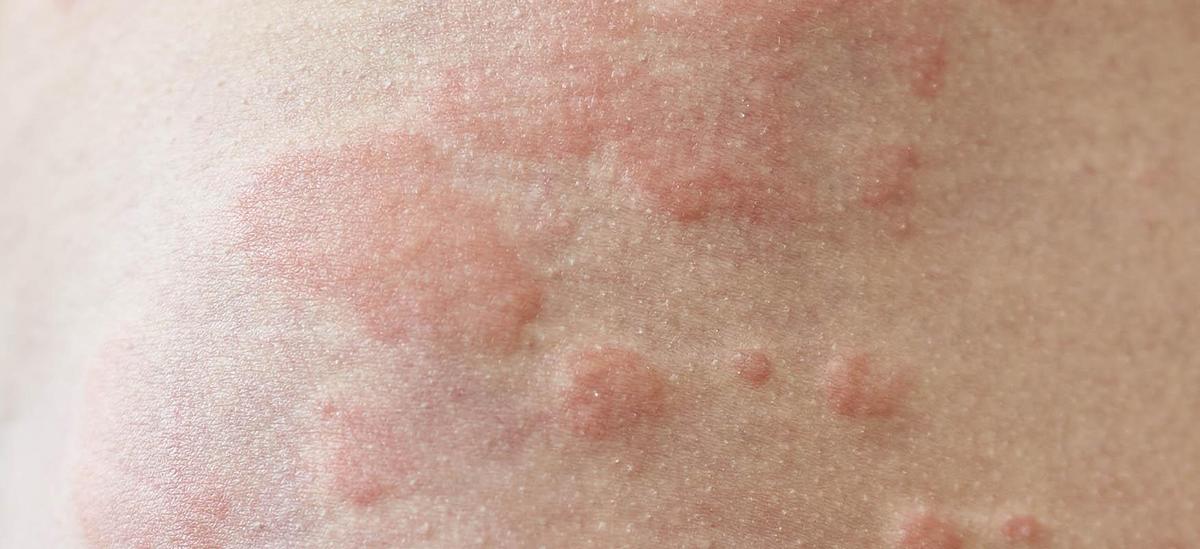
What are the types of urticaria?
Urticaria is divided into several types, depending on the factors that cause them. Thus, there are distinctions such as:
- Cold urticaria – occurs on skin that has been in contact with cold air or water.
- Cholinergic urticaria – is a response to sweat caused by exercise, stress or hot showers.
- Contact urticaria – changes occur after contact with an allergen or other irritant, including latex, cosmetics, meat, nettle, etc.
- Pressure urticaria – blisters occur due to pressure on a particular area of the skin, such as by a purse or seat belt.
- Sun urticaria – involves blisters in areas of the body that have been exposed to the sun – abdomen, upper thighs.
- Heat urticaria – occurs in areas of the skin that have been in contact with heat.
What are the causes of urticaria?
The occurrence of urticaria can be associated with many factors, so when typical symptoms occur, factors such as daily diet, medications taken and leisure activities should be analyzed. It is sometimes the case that people who spend too long in the sun or the cold just struggle with intractable urticaria. When urticaria does not disappear after a period of time, it is worth consulting a doctor. This is especially true for children and seniors, for whom the use of generally available antihistamines can prove dangerous to their health. It is also worth going to the doctor if the red lesions occur once again. The specialist will then decide whether the discomfort is related to an allergy. The cause of urticaria is also often stress, infection, insect bites and a reaction to medications taken. urticaria in children Red skin lesions can also be a symptom of sun allergy. ** Solar urticaria is one of the most common diseases that occur during the summer.** Blisters on the skin form when exposed to the sun and cause severe itching. They persist on the skin for several hours, after which they resolve on their own. UVB-sensitive people may notice urticaria in areas where the sun interacts freely – on the neckline, arms and legs. In such situations, the use of sunscreen is sufficient. Those who are allergic to UVA radiation, on the other hand, may notice urticaria on cloudy days as well. UVA rays even penetrate glass and clothing, so blisters occur all over the body. Urticaria can persist for a long time in such cases, and treatment involves limiting skin exposure to sunlight. People who are allergic to UVA radiation should wear long blouses and pants that cover their bodies. However, when they notice symptoms of sun urticaria, they should immediately consult a dermatologist. This specialist will select the appropriate medication to alleviate the symptoms of sensitization.
How is urticaria diagnosed?
Acute urticaria does not usually require a diagnosis, as the symptoms resolve spontaneously within a maximum of two days. The exception is urticaria associated with food allergies or hypersensitivity to certain medications. In such cases, it is very important to recognize the disease early and identify the agent that causes it. This helps prevent possible recurrence of allergies.
How does urticaria develop?
Urticaria is a vascular reaction and the occurrence of a wheal is associated with the penetration of plasma from blood vessels into the skin. This is due to the increased permeability of blood vessels and their dilation. In contrast, the reaction is caused by chemicals released from mast cells. Mast cells become stimulated due to allergic reactions. Then urticaria is simply a cutaneous symptom of sensitization to various substances. It is usually a reaction of the body that is limited to the skin. Sometimes, however, it can be the first symptom indicating a developing allergic reaction – anaphylactic.
How to treat urticaria?
Hives is treated with various antihistamines in higher doses than those recommended. That is why the treatment of urticaria should always be under the supervision of a doctor. When therapy does not have the desired effect, then steroid drugs or cyclosporine are also used. Allergic lesions on the skin can also be treated with herbal preparations in the form of infusions or teas. Those that in their composition contain the herb of hollyhock, cuddly, leaves of nettle and blackberry, fruits of rose and raspberry, burdock or dandelion root work well.
Urticaria is a vascular reaction and the occurrence of a wheal is related to the penetration of plasma from blood vessels into the skin. This is due to the increased permeability of blood vessels and their dilatation. In contrast, the reaction is caused by chemicals released from mast cells. Mast cells become stimulated due to allergic reactions. Then urticaria is simply a cutaneous symptom of sensitization to various substances. It is usually a reaction of the body that is limited to the skin. Sometimes, however, it can be the first symptom indicating a developing allergic reaction – anaphylactic.
How to treat chronic urticaria?
For chronic urticaria, symptomatic treatment is usually ineffective. Even after higher doses of antihistamines. The European Commission has approved an indication for omalizumab for the treatment of chronic urticaria in people whose body has not responded to antihistamines. Chronic urticaria can be diagnosed by itchy erythematous skin lesions that occur for more than six weeks. Omalizumab is a recombinant, humanized anti-IgE antibody. The drug binds to class E immunoglobulins. It simultaneously prevents them from binding to receptors on basophils. This contributes to reducing the amount of histamine that is released from basophils after allergic stimulation by up to 90%.
The European Commission's positive opinion is based on the results of three clinical trials (ASTERIA I, ASTERIA II and GLACIAL) involving nearly 1,000 patients who suffered from chronic urticaria and did not respond to antihistamines. The studies proved the drug's beneficial effect of reducing the occurrence of wheals, as well as reducing pruritus. In many cases, there was a complete resolution of urticaria symptoms.
Conclusion
Urticaria, a common but disruptive skin condition, comes in multiple forms and causes. From allergens to environmental triggers, understanding the condition is key to managing its symptoms. Treatments range from antihistamines to more advanced options like omalizumab for chronic cases. If urticaria persists, professional care is essential. By recognizing triggers, adopting protective measures, and seeking timely treatment, you can effectively manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Remember, with the right approach, relief is achievable.