TL;DR:
- Irregular periods occur when cycles are shorter than 21 days, longer than 35 days, or vary every month.
- Common causes: hormonal imbalances, puberty, menopause, stress, poor diet, PCOS, reproductive diseases, thyroid issues, and cancer.
- Symptoms: skipped periods, cycles outside 21-35 days, heavy bleeding, prolonged bleeding (>7 days), large clots, spotting, or significant cycle variability (>8 days).
- Medical attention is needed for infrequent (<35 days), frequent (>21 days), excessively heavy (>100 ml blood), or scant periods (<35 ml blood).
- Diagnosis: gynecological exams, ultrasounds, hormonal tests, biopsies, and checks for conditions like thyroid issues or diabetes.
- Treatment: depends on the cause (hormones, surgery for serious issues, psychotherapy for stress).
- Severe menstrual issues may indicate serious health problems, infertility risks, or life disruptions.
Irregular menstrual periods should always be a reason to go to a gynecologist for a check-up. There can be several reasons for this situation, and the most common include hormonal disorders. Other reasons for an irregular cycle can also be stress, improper diet, diseases of the reproductive system and even cancer.
Menstrual cycle
You are dealing with an irregular period when the menstrual cycle is once shorter than 21 days and once longer than 35 days. If the length of the cycle is different every month, it is essential to visit a gynecologist for a consultation. The reasons why there is a problem with an irregular period can be many, and this phenomenon involves not only different lengths of bleeding, but also different abundance. menstrual cycle
What are the causes of irregular periods?
** Irregular menstruation is very common in patients who have just started menstruating. Hormones can then cause cycle disorders even up to the age of 17. That is why, at this stage, an irregular period should not be a cause for concern and a symptom of disease. To be sure, however, it is better to go for a check-up with a gynecologist. Irregularity of the period is also a symptom of the onset of menopausal changes. During menopause, the ovaries create less estrogen with the next cycle, and the process of extinction can take up to several years. Other causes of irregular periods include pancreatic disorders, stress, liver disease, depression, PCOS, ovarian cancer, immune system disorders, poor diet, abuse of alcohol and other stimulants, uterine myoma, frequent climate changes, abnormal anatomy of the ovaries, damage to them during surgery. Many women, unfortunately, do not pay attention to the fact that there are irregular menstrual periods and explain such a situation with stress and an abnormal diet. This is the wrong thing to do, because disorders of the menstrual cycle can also be the cause of serious illness.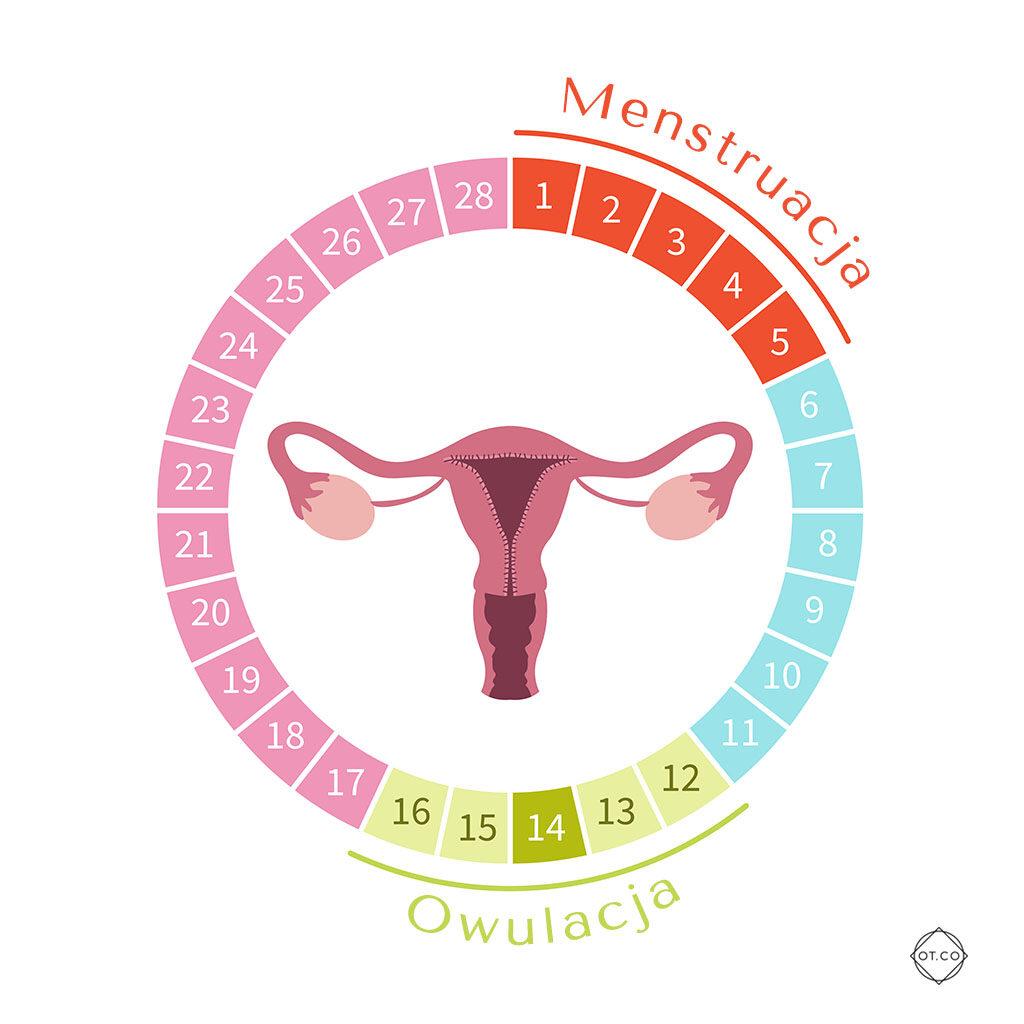
What are the symptoms of irregular periods?
Irregular periods take the form of primary or secondary absence of bleeding, as well as abnormal duration. Abnormalities usually occur in the form of one- or three-day bleeding in the middle of the cycle caused by a decrease in estrogen levels in the blood. ** An abnormal cycle is also distinguished by significantly prolonged bleeding of high abundance.** The most common symptoms also include missing a period for more than 35 days, menstruating more often than every 21 days, among others. Differences between cycles of more than 8 days, bleeding between menstrual periods, bleeding lasting more than 7 days, blood clots larger than 2.5 centimeters, and very heavy bleeding during which you have to frequently change your sanitary pads, menstrual cup or tampon due to seepage are also common symptoms.
When to go to the doctor?
A gynecology doctor should be visited when menstrual periods are too infrequent (less than every 35 days), too frequent (more than 21 days), too heavy (more than 100 ml of blood is lost), too scanty (loss of less than 35 ml). The gynecologist should find the cause of the problem and start appropriate treatment. He also collects a thorough medical history, information about the date of first menstruation, gynecological and obstetric past, chronic diseases and many other ailments. It is worthwhile for a woman who has noticed irregularities in her menstrual cycle to record the date of the beginning and end of her period in a diary and keep it under review.
How is the diagnosis of irregular periods carried out?
In order to make a proper diagnosis, the doctor must first find the cause of the problem. Then he implements the appropriate treatment. To do this, the gynecologist conducts an interview with the patient to determine the possible causes of irregular periods. The interview will help the doctor learn a little more about the possible causes of the disorder – contraception, obesity, restrictive diets, stress, too much training, etc. ** Then the woman undergoes a gynecological examination.** The doctor may also perform a vaginal or transvaginal ultrasound and take a cytology. If warranted, the gynecologist will also order additional tests to determine whether thyroid disease, diabetes, anemia may be the cause of the cycle disturbance. Adequately to the alleged causes causing the disorder, the gynecologist may also order hormonal tests – levels of FSH and LH, estradiol, testosterone, as well as progesterone. If the doctor notices abnormalities on ultrasound in the form of anatomical changes (suspected endometrial hypertrophy, polyps and myomas), he refers the woman for a diagnostic hysteroscopy or abrasion. The patient may also get a referral for an endometrial biopsy. Material taken during the procedures is subjected to histopathological examination. If the gynecologist suspects endometritis, he will refer the woman for cervical canal culture examination.
How is the treatment of irregular periods carried out?
Any disturbing change in the menstrual cycle should be consulted with a gynecologist. Basic examinations by the doctor (history, gynecological examination and ultrasound) will help to implement the appropriate treatment. Depending on the cause that causes cycle irregularities, the problem can be treated in a number of different ways. In the case of hormonal changes, cure with hormones is used – for PCOS, among others. In more difficult situations i.a. ovarian cancer, surgery is necessary. Irregular period can also result from mental disorders, depression, stress. In such a situation, cooperation between a gynecologist and a psychiatrist is undertaken. Together they decide on the form of therapy. Irregular periods are also a symptom of hyperthyroidism. Severe disorders and accompanying other symptoms – fatigue, lethargy, nervousness – may cause the doctor to recommend taking medication that reduces hormone production. An abnormal menstrual cycle can also result from disorders of the immune system. In that case, cooperation between several specialists is necessary – as in the case of mental disorders.
Are menstrual disorders dangerous to life and health?
In most cases, the prognosis is successful and with the inclusion of appropriate treatment or removal of the cause, the cause of the disorder can be eliminated and the cycle can be regulated. However, it is worth remembering that permanent disorders of the menstrual cycle can be indicative of serious health problems, which result, among other things, in problems with pregnancy. Menstrual disorders are usually not an immediate threat to the patient's life, but can result in infertility.
Conclusion
Irregular periods often signal deeper, treatable health issues. Causes range from stress and diet to hormonal disorders or serious illnesses. Symptoms like cycle inconsistencies, heavy bleeding, or missing periods shouldn’t be ignored. Early gynecological consultation ensures timely diagnosis and personalized care. Remember, irregularities might not threaten life immediately but can impact overall health and fertility. Take action—tracking cycles and seeking help empowers you to protect your well-being and future.